Rain Gardens: How to take advantage of rainwater in the garden
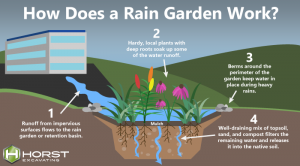
Rain gardens are depressional areas with crops that absorb water from precipitation. To do this, they must be strategically placed to capture runoff from roofs, roads, and other impervious surfaces. The land is filled with a sheet of a few centimeters of water, which allows a significant part of the rainwater to filter to deeper layers, and to continue its natural cycle, preventing it from reaching the sewers. In this article I will give you some tips to create your rain garden.
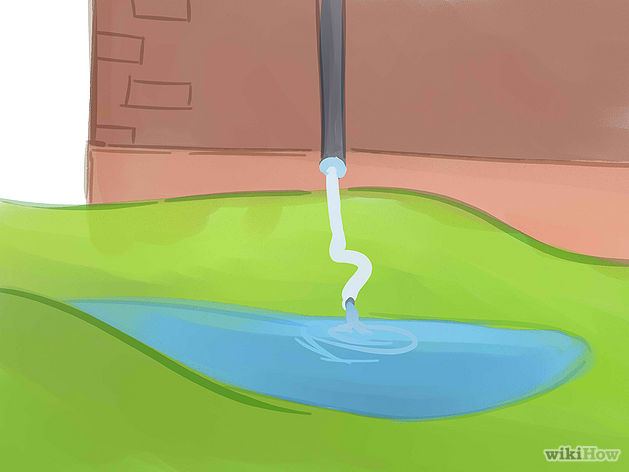
Where do I locate my rain garden?
The location is one of the most important aspects, since it will depend on it whether or not the orchard captures rainwater. In this sense, they must be located in such a way that they capture the water coming from impervious surfaces such as stairs, descents, roofs, etc. so you should examine the plot to locate these areas.
You should also make sure that the soil where you are going to implant it is not too clayey, since, if it is, it will tend to flood because its infiltration rate is very low.
To know if your soil is clayey or not, you must take a handful of soil, moisten it and try to make a ball. If the ball crumbles or you are unable to make it, it is a soil with a relatively high percentage of sand, so it will have a good infiltration capacity.
On the contrary, if the ball is sticky, soft and easy to work with, it will be a clay soil, with a tendency to waterlogging, so it would be advisable to mix it with sand or incorporate drainage.

Where NOT to find rain gardens
- On sanitation networks or septic tanks. Space it at least 15 cm.
- On shallow installations, gas services, electricity, telephone, water…
- Near steep slopes, as water can cause landslides.
- Less than 3 m from the foundation of surrounding buildings.
- Where the groundwater is within 30 cm of the rain garden.
- Areas where there is an underground impermeable layer that prevents filtration.
Construction of rain gardens
Dimensions and depth
The dimensions of the rain garden are determined by the total impervious surface from which the runoff water comes, and it is normally established at 7 to 20% of it. This would be at least the area needed to collect rainwater from those surfaces, but you can extend it.
The planting bed must be between 15 and 20 cm below ground level and the edge of this unevenness must not have any type of obstacle that prevents the passage of water.
soil amendments
In addition to the unevenness that we must create for the bed, it is recommended that the next 30 cm of soil be removed to make a series of amendments that contribute to improving the structure and properties of the land and allow healthy growth of plants. You must pay attention that the bed is level in all directions to avoid irregular accumulations of water.
Once leveled, you must incorporate a layer of about 8 cm of sand, another 5 cm of compost or organic fertilizer and another 3 cm of your soil and mix it as evenly as possible, subsequently leveling the ground. If the soil is suitable and you have made a good mixture, there is no reason why waterlogging will affect the development of the crop.

slope retention
When digging the trench we run the risk of the sides collapsing. To avoid this, we can build a retaining structure with wooden slats, plastic materials or stones.
Another solution would be to create embankments with less pronounced slopes where grass or other types of vegetation can be planted to help support the sides, thus increasing the biodiversity of the orchard and its ecological richness. We can take advantage to plant species that can serve as a reservoir for natural enemies or pollinators, contributing to maintaining the ecological balance in the crop.
Crop selection
A well-constructed rain garden does not differ from a conventional one, so, as always when you are going to establish a crop or a garden, you must take into account the environmental conditions of the area such as temperatures, relative humidity, sunshine, etc. the time of year, the type of soil, etc. From there, you have a wide range of crops to choose from. Of course, you must carry out proper maintenance of it and complement it with irrigation in times of low rainfall.
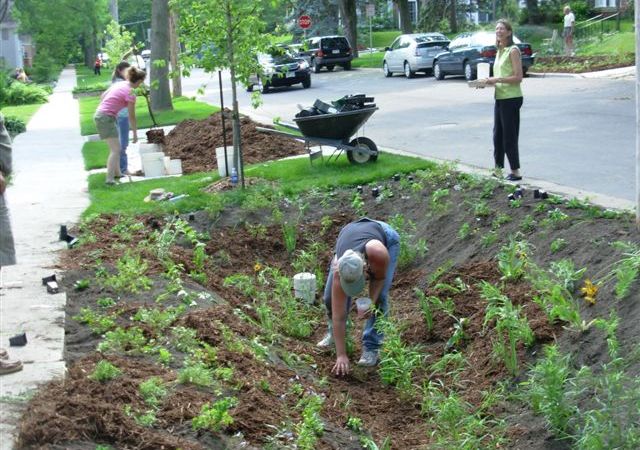

As you can see, the reduction and replacement of natural landscapes by cities modifies the dynamics of water and its composition. The incorporation of orchards and rain gardens can contribute significantly to reducing stormwater runoff, protecting water quality and helping it follow its natural cycle. So dare to set up your rain garden at home!

![Photo of Kokedama Care: [Soil, Humidity, Pruning and Problems]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/kokedama-care-soil-humidity-pruning-and-problems-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Outdoor Bonsai: [Characteristics, Care, Types and Sun Exposure]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/outdoor-bonsai-characteristics-care-types-and-sun-exposure-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Autumn Flowers: [Names, List, Care and Characteristics]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/flores_de_1589019104-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of When to Grow Tulips: [Temperature and Hemisphere]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/when-to-grow-tulips-temperature-and-hemisphere-390x220.jpg)