vermicompost
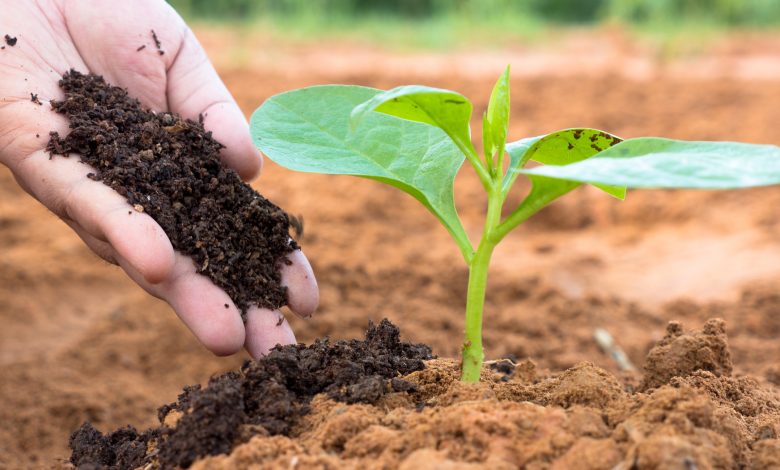

Compost is a good product as an organic soil amendment. There are several ways to generate it, including vermicompost.
A compost is not something that has been invented or manufactured by the human being, but rather it is a product that has always been present in nature as its own part. It is found in the natural cycle and with it organic elements that have finished their «useful life» are regenerated to become part of the chain of life again.
What is vermicompost?
Vermicompost is also known as earthworm humus, as it is a very common practice to generate it thanks to the outstanding help of these annelids. But not all vermicomposts are the result of your active participation.
As we advance, compost is part of the result of the microbial decomposition of dead organic matter in the presence of oxygen or aerobic conditions, as it can also be defined. It is part of the natural cycle of nature.
This decomposition via vermicompost is the one that most imitates nature in terms of popularity, since it occurs at room temperature, with earthworms and other microorganisms being responsible for this transformation. Microorganisms in which numerous insects and other animals fit, as well as fungi and bacteria.
It differs from another model, thermophilic compost, which is produced by fermentation and at high temperatures, reaching 65°C or more. In these cases, it is basically fungi and bacteria that are responsible for the process.
Without discrediting other types, vermicompost is a high quality compost.
Differences between vermicompost and thermophilic compost
There are notable differences between vermicompost and thermophilic compost, since their degradation or decomposition processes are different, to the extent that not all fauna and microorganisms participate in the process in the same way.
For a better understanding, below, we make an explanation of each of them.

How is vermicompost produced?
It is the method that best imitates nature, and consists of depositing remains of organic matter in composters, containers or piles, maintaining a certain humidity so that worms, insects, bacteria and fungi act on the decomposition of this organic matter.
In the case of detritivorous or iliophagous insects, they play a very important ecological role because they contribute to the decomposition of organic matter.
The presence of worms during the vermicomposting process is very relevant. These aerate the material and prevent or greatly reduce fermentation.
This transformation of the organic matter into a more humified one is basically the result of its digestion by this fauna. The result is an organic matter richer in humus and in substances derived from the action of microorganisms, bacteria and fungi, such as phytohormones (auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, etc.), of great nutritional and stimulating value for plants.
In short, a compost with a diverse microbial community (microbiome), which would otherwise be eliminated through the high temperatures reached in thermophilic compost piles.
How is thermophilic compost produced?
The principle is the same: favor and accelerate the decomposition of the base organic matter into a more humified one.
To produce thermophilic compost, organic matter is deposited and piled in rows several meters high, simulating mountain ranges. Moisture is applied to them and a fermentation is allowed to begin.
The fermentation temperature can exceed 65°C and to prevent it from exceeding unwanted thresholds, it is turned over using specialized machinery.
During this periodic turning, on the one hand, the fermentation is paralyzed, the microorganisms that cause it are mixed, and the fermentation process is restarted.
After a time of turning, a quality compost is also obtained, without seeds because practically all of the existing ones are eliminated either by fermentation or by the attack of microorganisms.
During a stabilization period, they are packaged or marketed in bulk.
Production method and technology of vermicomposting
There are different production methods and vermicomposting technology. Basically, it should be known that during the vermicomposting process the seeds of many species are not eliminated, especially weeds or wild field herbs. For this reason, it is essential to avoid, as far as possible, that the organic material used does not contain seeds.
In areas with a temperate climate, vermicomposting can be done outdoors. In others, with adverse weather conditions, whether due to cold or heat, it must be done in a protected structure such as warehouses or greenhouses.
Structures for composting are placed in them, such as drawers that can be stacked, leaving space between the different rows. These drawers should not be very deep because the worms remain in the top 15 and 20 centimeters.
Thus, the drawers are filled with remains of organic matter, they are provided with moisture and, especially for the first time, worms and remains of vermicompost are incorporated to enrich the new product of microorganisms that initiate organic decomposition.
These drawers are gradually filled and a constant humidity is maintained, without draining it to avoid leachate. Continuous flow methods will normally be top fed and collected from the bottom zone.
Since mostly the worms stay in the top 15-20 centimeters, when collecting the material from the bottom, it is not necessary to separate the worms from the final product.
Another vital aspect in vermicomposting is the material used. This must be suitable, especially for worms so that the vermicompost obtained is optimal.
For vermicomposting to develop properly, in addition to the type of organic matter to be composted and the existing fauna, the temperature must be between 15 and 30°C, with a moisture content of 60 to 80%, a pH 6-8, with fully aerobic conditions, and ‘sufficient feed’ with a loose structure.
If different materials are used, they must be mixed and, if some are of a certain thickness, modified to achieve the required quality.
Vermicompost quality control and regulations
If the vermicompost is made in the user’s field to apply it in their orchard or garden, quality control and application of regulations is subjective and practically nobody puts it into practice.
On the other hand, when it is produced by companies, it must be done and, in fact, quality control is essential.
Thanks to this control, it can be certified that the vermicomposting process has been carried out successfully, where the worms and microorganisms have completely processed the organic materials.
As for the regulations that regulate it, they go by country. While some have their own national legislation and regulations, others do not have any. For many, vermicompost is considered as compost, or they regulate it as organic or organo-mineral fertilizer.
Vermicompost application
Vermicompost is an organic amendment with a high nutritional value as well as a soil regenerator, so it should be used in the planting of high-value crops or gardens. The application of this type of organic compost for urban gardens is highly appreciated.
The high amount of time and resources necessary for the production of vermicompost with respect to thermophilic compost, makes it higher.
It is also true that the vermicompost application doses are much lower.
This can be used under many criteria: mix it with the substrate to improve it, the same with the farmland located in the area of root development of the plant, as a fertilizer or improver of physical, chemical and microbial qualities of the farmland. In short, vermicompost is an ideal product to keep soils more alive.



![Photo of Temperate Continental Climate: [Characteristics, Flora, Fauna and Adaptability]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/temperate-continental-climate-characteristics-flora-fauna-and-adaptability-390x220.jpg)