Actinomycetes: [Characteristics, Development, Functions and Diseases]
Important points about Actinomycetes:
- What features do they have? The actinomycetes constitute a group formed by heterogeneous filamentous bacteria, somewhat similar to fungi.
- When are they born? Actinomycetes are strictly aerobic beings and depend for their development on climatic conditions that determine the number and quantity of the population.
- Where do they develop? Actinomycetes grow and develop in the soil forming small colonies of various colors.
- What do they need for their development? The ideal temperature for the development of actinomycetes is between 28 and 37º C. Their preferred seasons are spring and autumn.
- What functions do they fulfill? They are responsible for decomposing animal and plant waste, they have a very active participation in humidification processes, they help secrete antibiotic substances, among other functions.
- What diseases do they cause? Pulmonary nocardiosis, actinomycetoma and actinomycosis.
From a biotechnological point of view, actinomycetes constitute a very important group because they produce Group B vitamins, antibiotics and pigments that are widely used at an industrial level.
They are highly valued in the pharmaceutical and food industries, and more recently in agriculture, and are sources of substances with biological activity of great use to man.
Among the actinomycetes there is a very famous group known as Streptomyces from which Selman Wasksman, Nobel laureate in medicine in 1940, discovered actinomycin from which a multitude of antibiotics were produced.
What characteristics do actinomycetes have?
 The actinomycetes constitute a group formed by heterogeneous filamentous bacteria, somewhat similar to fungi.
The actinomycetes constitute a group formed by heterogeneous filamentous bacteria, somewhat similar to fungi.
That is, actinomycetes have some physiological properties similar to fungi in the kind and shape of the mycelium.
Actinomycetes bacteria have a characteristic mycelium that tends to fragment into several bacterial elements that differentiate it from fungi.
Actinomycetes (Ac) are prokaryotic bacteria, with a very complex morphology, sensitive to penicillin that, in general, develop in the soil and have a free life. The nuclear region of actinomycetes occupies a larger area and is more visible than the aerial mycelium.
A characteristic of the aerial mycelium of actinomycetes is the high presence of branches that seem to ensure a greater cell volume for the propagation of spores.
The walls of prokaryotic actinomycetes contain peptidoglycan that differentiates them from eukaryotic filamentous fungi. Actinomycetes are similar to fungi due to their morphology, reproduction, and growth in solid and liquid culture media.
The word actinomycete, etymologically, means sunbeam-shaped fungus. According to Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, actinomycetes are cataloged within Phylum: Actinobacteria, Class: Actinobacteria, Order: Actinomycetales, and Family: Actinomycetaceae.
Actinomycetes are part of natural ecosystems around the world and play a very important role in recycling organic matter.
When are actinomycetes born?
Actinomycetes are strictly aerobic beings and depend for their development on climatic conditions that determine the number and quantity of the population.
Where do actinomycetes develop?
Actinomycetes grow and develop in the soil forming small colonies of various colors.
They reproduce easily at temperatures above 25º C and with an alkaline pH (pH=9).
In temperate soils, actinomycetes grow at 100,000 to 100 million per gram, provided the pH is not less than 5.
They do not breed as easily in waterlogged soils, tundras, and acidic peat bogs. Actinomycetes abound in soils with organic matter and fertilized with it, especially if the humidity becomes 85-100% of the soil’s capacity.
They are bacteria that withstand drought and are found in desert areas. It has generally been said that actinomycetes are soil-dwelling microorganisms.
However, it is now known that they are also distributed in aquatic environments: oceans, rivers and lakes, associated with sediments of organic material in the process of decomposition.
What do actinomycetes need for their development?
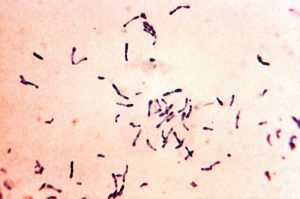
Actinomycetes abound in alkaline and dry areas going from a normal 10% to 95 percent of the total flora.
The ideal temperature for the development of actinomycetes is between 28 and 37º C. Their preferred seasons are spring and autumn.
They feed on organic compounds and abound on the organic materials provided by man and nature.
What functions do actinomycetes perform?
Bacteria known as actinomycetes perform very important functions, including:
- They are responsible for breaking down animal and plant waste.
- They have a very active participation in the humidification processes.
- They function for the mineralization and production of humus.
- They have the ability to degrade substrates such as starch, inulin, chitin and cellulose.
- They have phytopathogenic functions. They are effective against numerous plant pathogens, are cheap, durable, do not pollute and do not alter the ecosystem.
- They help secrete antibiotic substances.
- The mycelium of actinomycetes represents a raw material for the synthesis of humic compounds.
- They improve crops in order to establish a new type of sustainable agriculture.
What diseases do actinomycetes cause?
Actinomycetes are pathogenic bacteria for man and also for some animals. In hosts, actinomycetes can cause diseases such as:
Pulmonary nocardiosis
Its most common symptoms are fever, cold sweats, nausea, dizziness, headaches and it manifests itself through skin rashes and seizures or epileptic seizures.
actinomycetoma
It is a disease that penetrates the skin of the hosts when they are punctured with pimples, wood chips or any other object that causes a wound or skin trauma.
Actinomycosis
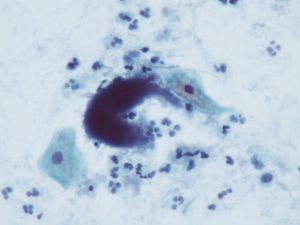
It presents as a chronic granulomatous infection. In this action, the Gram bacilli adopt filamentous forms that produce the so-called sulfur granules.
Diseases caused by actinomycetes are generated when the host’s immunological condition is weak and that is when the virulence mechanisms are more active.
But actinomycetes can also help prevent and defend plants from diseases and bacteria.
They transform organic matter and convert, into highly available forms for plants, the nutrients that are supplied with manure, compost or other organic forms.
Bibliographic references
- Allergenic fungi and actinomycetes, J Pontón, MD Moragues, J Gené, J Guarro… – 2002 –… -alergenicos.reviberoammicol.com
- Effectiveness of actinomycetes isolated from the potato rhizosphere on Rhizoctonia solani Kühn in vitro, C Castillo – Revista Mexicana de Fitopatología, 2004 – redalyc.org
- Isolation, selection and identification of actinomycetes, non-sulfur photosynthetic bacteria and lactic acid bacteria with biofertilizing potential, from soils…, V Otero Jiménez – Postgraduate Interfaculty in Microbiology, 2011 – repository.unal.edu.co
- Isolation of actinomycetes associated with the rhizosphere of apple trees antagonistic to Fusarium equiseti, DA Pérez-Corral, NY García-González… – Revista mexicana de…, 2015 – scielo.org.mx
- Actinomycosis, R Torres Iberico, E Escalante – Dermatol. Peru, 1999 – pesquisa.bvsalud.org
- Cervicofacial actinomycosis, M del Carmen Padilla, L Alonzo… – Dermatology Magazine…, 2007 – medigraphic.com

![Photo of Types of Tomatoes and the Most Cultivated Varieties: Complete Guide [breadcrumb]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/types-of-tomatoes-and-the-most-cultivated-varieties-complete-guide-breadcrumb-390x220.jpg)