Onion Miner (Acrolepia assectella): [Characteristics, Detection, Effects and Treatment]
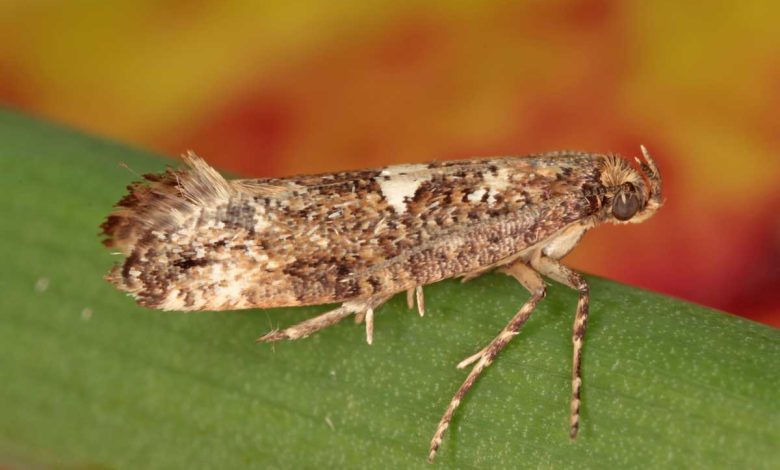

What is onion miner?
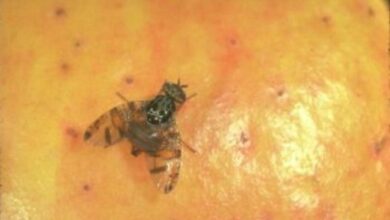
 The onion miner or moth is a butterfly with the scientific name Acrolepia assectella, characterized by causing great damage to the ancient cultivation of onions.
The onion miner or moth is a butterfly with the scientific name Acrolepia assectella, characterized by causing great damage to the ancient cultivation of onions.
Its caterpillar is very persistent in its feeding desire, to the point that it can ruin the plant to the point of death if its devouring progress on the leaves is not stopped.
It is commonly known as «the fly», when in fact it is a nocturnal butterfly that attacks not only onions, but also other similar crops.It performs its first flight between April and May and then repeats its prowling over the crops, between July and August.
How can we identify it?
Some of the following signs can be very helpful in identifying this natural enemy of growing onions. Let’s see.
- The butterfly has dimensions estimated at about 16 mm.
- It is grayish brown, with light bands and a bright ocher head.
- It has violet- blue forewings, which fade from more to less dark, with ocher-yellow scales.
- The upper ones, on the other hand, are between 15-18 mm long and have a grayish appearance.
- The larva of this species is brownish-yellow in color and is between 15-18 mm long.
- The female larva is responsible for laying her eggs on the leaves at the end of May.
- When they hatch from the eggs they will begin to dig a tunnel downwards.
- The leaves will be the succulent dish of the larvae, whose most notorious evidence will be the multiple holes produced by their persistent bite.
- After feeding incessantly, the larvae fall to the ground, in order to protect themselves from the winter cold and prepare for the metamorphosis that will turn them into butterflies as soon as spring appears.
What plants does the onion miner affect?
 The caterpillars of this butterfly are responsible for the sometimes irreversible damage that shakes onion plantations.
The caterpillars of this butterfly are responsible for the sometimes irreversible damage that shakes onion plantations.
The onion is an ancient vegetable, whose origin is focused on Central Asia, but which later passed to the Mediterranean region, its second oldest production center.
There is evidence of its cultivation around the year 3,200 BC, in the Egyptian, Roman and Greek cultures, but towards the Middle Ages throughout the Mediterranean region large-bulb species proliferated, giving way to modern varieties.
But they also attack garlic plants, leeks and the like. They mercilessly enter the interior of the leaf sheaths, leaving them pierced, and then climb towards the neck.Among the largest damages are:
- The process of plant development stops.
- The leaves turn yellow and lose density, until the plant dies and, sometimes, rots, thanks to the incorporation of fungi that penetrate through the wounds left by the caterpillar.
- In the case of leeks, spawning leaves holes in the leaves, but they can be removed and the plant cut down to ground level so that it can recover. It grows back if it is helped in time.
How can we combat the onion miner?
Cultivation practices that can prevent the proliferation of this pest are key. It will always be profitable to keep plants healthy through preventive actions that protect them from bugs and diseases associated with erratic habits that damage the harvest.
Land cleaning
 An inalienable practice is to clean the growing area of weeds, so that we have the best harvests.
An inalienable practice is to clean the growing area of weeds, so that we have the best harvests.
Why? The plant has a short root system and that is why you have to take great care of it from invaders that compete with them.
It is very important to aerate the selected terrain with successive weeding to interrupt capillarity and suppress the bush or weeds.
A highly rewarding habit is to do the first of these cleanups when the young plant is about 10cm tall, to prevent weeds from doing their thing.
Guaranteed sowing
 In the same way, it is mandatory to acquire certified seeds of the onion species that best adapts to the prevailing climate, because in this way the proliferation of diseases as a result of contaminated seeds is avoided.
In the same way, it is mandatory to acquire certified seeds of the onion species that best adapts to the prevailing climate, because in this way the proliferation of diseases as a result of contaminated seeds is avoided.
This planting, if it is done on the ground, must have a previous disinfection of it. A layer of mulch of about 3-4 cm is usually placed on an estimated quantity of seeds that can reach 4 g/m2.
In general, it is customary to plant first in a seedbed, so that a transplant can be done later, at the time of year that corresponds to the cultivar species.
Fertilization
As a rule, the onions with the best level of conservation are those that thrive in less fertile land, but with a major associated problem: their development is less.
So it is preferable that they grow on manure from the previous year, which favors a production of large bulbs, typical of optimal fertilization.
A correct dose of nitrogenous fertilizer also favors a good conservation of the onion plantation, but the excess produces watery bulbs that do not last long. So you have to be very careful when applying it.
Irrigation
 Key will also be irrigation. The first should be done just after planting. Afterwards, the periodicity will occur every 15-20 days.
Key will also be irrigation. The first should be done just after planting. Afterwards, the periodicity will occur every 15-20 days.
And between spring and summer, irrigation will be greater for the second planting, due to the increase in environmental temperature and vegetation.
Reducing the water supply to the plant during the latter period will help preserve the bulb, although it will taste more sour. But this will help prevent the plant from getting sick.Before harvesting, irrigation should be suppressed between 15-30 days before and antiperspirants should be applied.
Crop rotation
 It must be prevented by applying the crop rotation technique and establishing associations with celery and carrots.
It must be prevented by applying the crop rotation technique and establishing associations with celery and carrots.
Among natural medicines, it is of vital importance to introduce Bacillus thuringiensis, so that it exterminates the larvae by preventing them from developing.
Likewise, if the plague grows, it is also highly recommended to resort to spraying with neem.With these healthy practices, diseases are prevented and unwanted visits are repelled.
What are the best products to eliminate onion miner?
 Chemical treatments should only be applied if the cultivar area is under the dominance of a persistent pest.
Chemical treatments should only be applied if the cultivar area is under the dominance of a persistent pest.
To undertake this strategy, some of the following products must be applied, whose application must be repeated 15 days later, without fail.
The following active ingredients can be used:
- Carbaryl 50% PM, between 200-250g/Hl.
- Trichlorfon 35% LE, between 250/300 g/Hl.
- Methyl-azinphos 80% PM, between 150-250 cc/Hl
- Methamidophos 50% LE, at 100 cc/Hl
- Phosmet 50% LE, at 250cc/Hl.
- Endosulfan 35% LE, between 150-300 cc/Hl
- Ethyl-parathion 50%, at 150cc/Hl.