The Climate: [Concept, Elements, Importance and Examples]
What we tell you in this article:
- We will explain what climate is and why it is formed.
- You will also be able to know the elements that affect the climate and modify it.
- The reasons why the climate is something so important with respect to agriculture, livestock and fishing.
- Because there are areas on Earth where the weather is extreme and makes life difficult (although it exists).
- Also a bit of history and how the climate has affected human behavior.
Climate or weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing, for example, how hot or cold it is, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy.
On Earth, most weather events occur in the lowest layer of the planet’s atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere.
Weather refers to the daily temperature, rainfall, and other atmospheric conditions. It is also the term that designates the average of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time.

What is the weather?
We have all experienced it. In fact, we feel and see it daily.
But really, what is weather?
Weather is the mix of events that happen every day in our atmosphere. The atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the Earth. It is made up of mostly nitrogen, some oxygen, and a few other gases, and is held together by gravity.
Heat from the sun heats gases in the atmosphere to different temperatures and in different places, causing the air to move.
This movement of air is called wind, and wind causes changes in the weather. Water vapor or humidity in the air also affect the weather. Changes in atmospheric pressure also affect the weather.
Therefore, the time we experience depends on what happens in the Earth’s atmosphere.

What makes the climate change?
The climate is governed by the differences in atmospheric pressure, temperature and humidity between one place and another.
These differences can occur due to the angle of the Sun at a particular point, which varies with latitude.
The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the largest-scale atmospheric circulations: the Hadley cell, the Ferrel cell, the polar cell, and the jet stream.

Mid-latitude weather systems, such as extratropical cyclones, are caused by jet stream instabilities.
Since the Earth’s axis is tilted relative to its orbital plane (called the ecliptic), sunlight strikes it at different angles at different times of the year. On the Earth’s surface, temperatures typically range annually between ±40 °C.
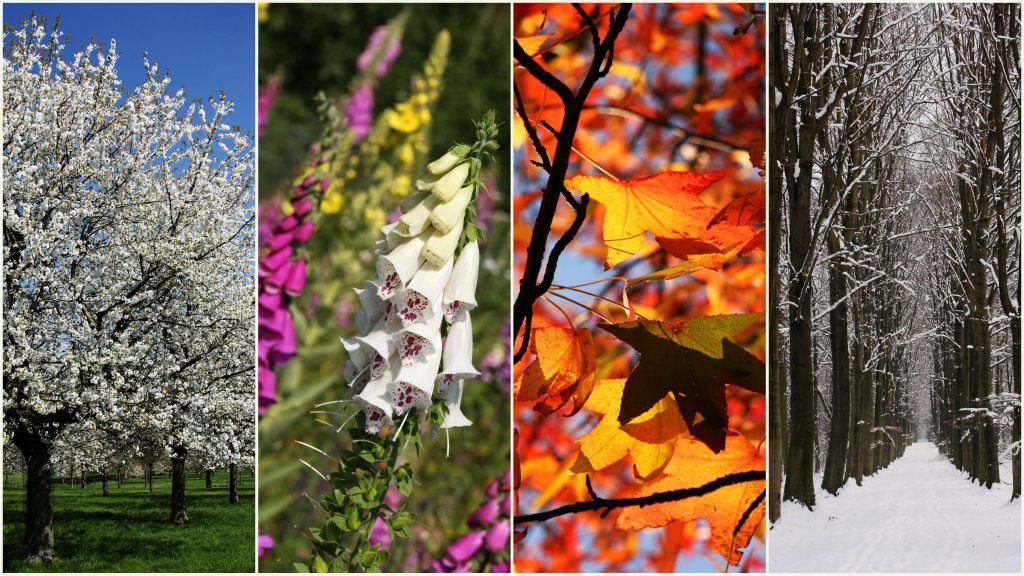
What types of weather are there?
There are different types of climate, according to pre-existing conditions in a certain region of the globe. It is so influential in people’s lives that it characterizes the type of social and economic activity in the regions, and even influences the food consumed by its inhabitants.
 The climates are structured in climatic groups.
The climates are structured in climatic groups.
Let’s see then what are the types of climate identified by experts in climatology.
These are presented according to pre-existing variables, such as humidity, temperature, winds, ocean currents, soil types, among others.
The most widespread or well-known classification refers to climates that differ according to the prevailing temperature. Thus we have: temperate, cold and warm climates, with their respective subdivisions.
The educational portal Wikipedia, when referring to this classification, describes general characteristics of these three great climates on Earth. Let’s see a summary of that dense information.
temperate climates
 Temperate climates are typical of the middle zones of the globe, located between parallels 30 and 70 degrees, approximately. They are conditioned by the winds that come from the west and the contrasts that arise in the different seasons, in terms of rainfall and temperature.
Temperate climates are typical of the middle zones of the globe, located between parallels 30 and 70 degrees, approximately. They are conditioned by the winds that come from the west and the contrasts that arise in the different seasons, in terms of rainfall and temperature.
It is a climate of annual temperatures located around 15 ºC.
Variations range from 300 to 1,000 meters above sea level (masl), but also depend on factors such as wind, insolation or sun exposure, the distance that separates the seas and continental regions, among others.
There are two large groups of climates of this type: they are subtropical or warm-temperate climates and temperate climates per se. And they have subdivisions. These are: humid subtropical climate, oceanic climate, continental climate and Mediterranean climate.
To know more, you can see: Continental climate and Humid tropical climate.
hot climates
 Warm climates manifest themselves with more or less constant temperatures throughout the year. It is a climate that occurs in regions near the equatorial strip of the globe, between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
Warm climates manifest themselves with more or less constant temperatures throughout the year. It is a climate that occurs in regions near the equatorial strip of the globe, between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
They are subdivided according to variables such as the distance they have with respect to the terrestrial equatorial line, the amount of rainfall, and also biotic factors such as vegetation and fauna of the place, as well as living beings that must adapt to the climatic conditions of the habitat where they they remain.
Precisely the vegetation is abundant and, together with more or less important annual rainfall, there is a process of self-regulation of the temperature in summer, especially during the day, a situation that also benefits the animal species of these humid habitats.
There are warm climates of equatorial type, dry tropical climate, arid tropical and desert and semi desert.
Within the temperate climates we distinguish two large groups: the subtropical climates, or temperate-warm, and the temperate climates proper, or temperate-cold. In turn, within each of these large groups several climatic subtypes are included.
To know more, you can see: Jungle climate and Dry tropical climate,
Cold climates
 Cold climates include, as their name indicates, climates whose temperatures are low, or very low, below the freezing point.
Cold climates include, as their name indicates, climates whose temperatures are low, or very low, below the freezing point.
They are the coldest climates on the planet and their temperatures range from 8 ºC to -88 ºC. Large rainfalls do not usually occur, with zero or almost zero percentages of atmospheric humidity, especially when we are at the Poles or ends of the Earth.
This climate the following subdivision: polar, mountain and tundra climates.
- Polar climates develop at the poles or extremes of the planet, better known as the Arctic Circle (north) and the Antarctic Circle (south).
- Tundra climates are located in subpolar regions and in a portion of the North and South Poles.
- Mountain climates, as their name indicates, develop on the planet’s mountain peaks. They exceed 2,000 meters above sea level (masl) in the vicinity of the terrestrial poles and near the equator they rise to 3,500 meters above sea level or more.
- Cold continental climate, is the one that develops in much of Europe (north and northeast) Canada, Alaska and Siberia (central and southern regions).
How do Earth’s orbital changes affect climate?
Over thousands of years, changes in the Earth’s orbit can affect the amount and distribution of solar energy received by the Earth, thereby influencing long-term climate and global climate change.
Temperature differences at the surface in turn cause pressure differences.
Higher altitudes are cooler than lower ones, since most atmospheric heating is due to contact with the Earth’s surface, while radioactive losses to space are mostly constant.

What is the weather forecast?
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere at a future time and place.
Earth’s weather system is a chaotic system; As a result, small changes in one part of the system can have large effects on the system as a whole.
Is the study of climate important? Has the human being tried to modify it?
Throughout history there have been attempts to control the climate and there is evidence that human activities such as agriculture and industry have changed weather patterns.
The study of how weather works on other planets has been helpful in understanding how weather works on Earth.
A famous landmark in the Solar System, Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is an anticyclonic storm that has been known to exist for at least 300 years. However, weather is not limited to planetary bodies.
A star’s corona is constantly being lost to space, creating what is essentially a very thin atmosphere throughout the Solar System. The movement of mass ejected from the Sun is known as the solar wind.

What examples of weather can we find to explain to a young child?
To answer the question «What is climate?» , it is best to look at examples that we all know.
Here are some examples of kid time:
- Sun.
- Rain.
- Wind.
- Clouds.
- Fog.
- Snow.
- Hail.
- Sleet.
- Thunders.
- Ray.

What are the four elements of weather?
There are four main elements of the weather that affect our daily lives.
They are temperature, wind, snow or rain, and sunlight or clouds.
They can exist in different combinations and affect what we wear, where we go and how we feel.
For example:It may seem like it’s very sunny in the middle of winter, but you should still bring a coat. Or it can be cloudy and windy, but still hot.
Viewing the weather forecast each day can help you decide how the four weather elements will affect your decisions that day.
Weather forecasts show a weather map with the different conditions you can expect throughout the day and week. Maybe you can make the most of the sun.
Or maybe you have to look for some indoor activity.

How can we predict the weather?
The measurement of the climate tries to observe the main factors that affect it. At first glance, it seems quite simple, right?
But, how to predict the weather in order to anticipate what is going to happen? And how does the human being do it with sufficient precision and detail?
Meteorologists measure all the components that affect the weather and put them together.
They use special weather instruments to measure and record the four elements of weather. This helps them predict what the weather will be like. Below we have listed the ways in which the different elements of weather are measured.
However, it must be said that on many occasions these forecasts are wrong.

Temperature
Measuring the temperature is quite easy: all you need is a thermometer. Mercury used to be used in thermometers, but mercury is a very dangerous substance. Today, digital thermometers are used to measure temperature.
Humidity
Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. It is measured by measuring the temperature of a thermometer with its end; wrapped in a damp cloth. It is then compared to a normal thermometer.
After doing some calculations, we can estimate the ambient humidity.
Wind
We measure the direction and speed of the wind.
Wind direction can be measured with a wind vane. It shows us where the wind is coming from, which can tell us a lot about the weather. The north wind tends to be quite cold, while the south wind is warmer.
An anemometer is used to measure wind speed. It rotates to show the speed at which the wind is moving.

Visibility
Visibility is the distance we can see without binoculars or other aids. When it is foggy, visibility can be very low.
We measure our visibility using our eyes. We look for points that are at a certain distance and see those that are very clear. Sometimes lasers are used to improve accuracy.
Rain
Rain accumulation is the amount of rain that reaches the ground over a period of time. It is measured with rain gauges that collect rain.
The rain rate is the amount of rain that falls from the sky, as well as its speed. We can use radar to estimate the rate of rain.
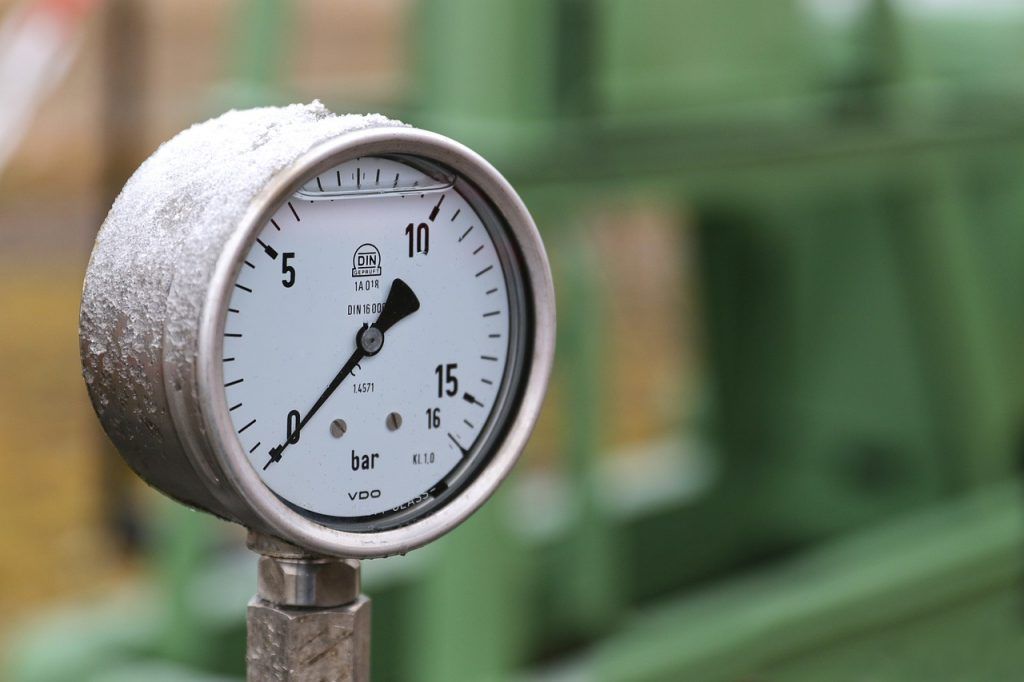
Pressure
Atmospheric pressure can tell us what kind of weather we can expect. With high pressure, we normally expect clear skies and light winds. But when the pressure is low, the weather is usually wet and windy.
Pressure is measured with a barometer, which has different bubbles to show the air pressure.
These are the main factors we use to predict the weather.

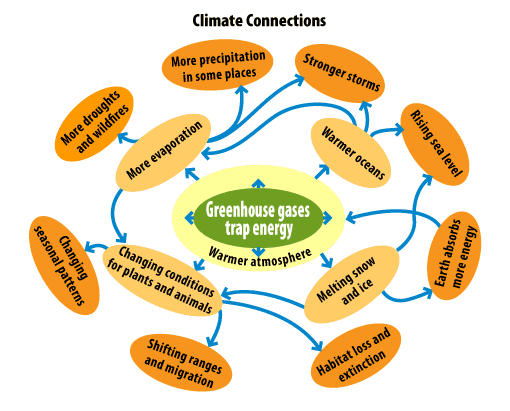
How does climate change affect climate on Earth?
Climate change is a reality.
Climate change means that we are likely to experience more frequent extreme weather conditions, such as heat waves, floods, hurricanes and storms.
The increase in heat associated with climate change can have serious consequences.
For example:In the Arctic, rising temperatures have caused the polar ice caps to melt, which has serious effects on the animals and people who live there.
Extreme weather around the world
On Earth, temperatures typically range annually between ±40 °C.
The variety of climates and latitudes on the planet can offer extreme temperatures outside this range.
- The coldest air temperature ever recorded on Earth is -89.2°C, at the Vostok station in Antarctica on July 21, 1983.
- The warmest air temperature ever recorded was 57.7 °C at ‘Aziziya, Libya, on September 13, 1922, but this reading is disputed.
- The highest mean annual temperature recorded was 34.4 °C in Dallol, Ethiopia.
- The coldest annual mean temperature recorded was -55.1 °C at the Vostok station (Antarctica).
- The coldest annual mean temperature in a permanently inhabited place is in Eureka, Nunavut, Canada, where the annual mean temperature is -19.7 °C (-3.5 °F).
- The windiest place ever recorded is in Antarctica, in Commonwealth Bay (George V Coast). Here the gales reach 320 km/h. In addition, the largest snowfall in a twelve-month period occurred on Mount Rainier, in Washington, United States. 31,102 mm of snow was recorded.
As climate change increases around the world, it is likely that we will start to experience more extreme weather in parts of the world where there is quite a bit of «calm weather».
This includes hotter summers, more flooding, and the loss of coastlines.
Here are some of the types of extreme weather you may hear about in different parts of the world:
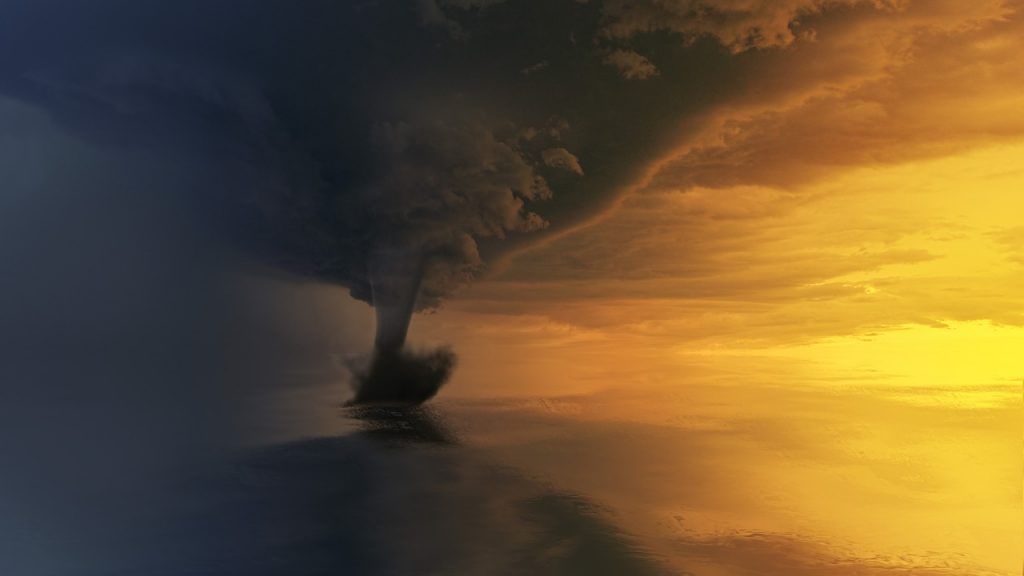

tornadoes
A type of extreme weather experienced throughout the world.
They consist of vertical funnels of rotating air that move at extreme speeds. The United States of America is the country that experiences the most tornadoes each year, and they can be very dangerous and deadly.
floods
When there is heavy rain for a long time, flooding may occur. Many countries around the world experience flooding, including the Philippines, India, Vietnam, France, Spain, Italy, and the United Kingdom.

Electric storms
The storms vary in intensity; some are relatively harmless and others cause massive destruction. Thunderstorms are a type of storm that includes thunder and lightning.
Each lightning bolt can contain a billion volts of electricity.
How does the weather affect agriculture and gardening?
Agriculture and fishing depend heavily on the weather.
The increase in temperature and carbon dioxide (CO2) can increase the yield of some crops in some places.
But to reap these benefits, certain nutrient levels, soil moisture, water availability, and other conditions must also be met.
Changes in the frequency and timing of droughts and floods could challenge farmers and ranchers and threaten food security.

Meanwhile, rising water temperatures are likely to cause changes in the habitat ranges of many fish and shellfish species, potentially altering ecosystems.
In general, climate change could make it more difficult to grow crops, raise animals and fish in the same way and in the same places as in the past. The effects of climate change must also be considered alongside other evolving factors affecting agricultural production, such as changes in farming practices and technology.
For example:Many plants and flowers cannot withstand extreme climates. Therefore, sudden changes in the weather, tending to extreme temperatures and/or meteorological disasters, cause the destruction of crops and ornamental gardens.
The weather throughout history
From approximately 10,000 a. C. that the human being began with agriculture and livestock, time has been a tremendously important factor. The human being began to depend to a great extent on the rains and possible droughts.
It was venerated and sacrifices were offered to the different gods, in different cultures so that each year the climate was suitable and the harvest sufficient.
A summer with extreme drought led to famine. But also, autumns with excessive rainfall and floods also damaged crops.
Sources and bibliographies
- Weather, on Wikipedia.
-
[PDF] History of the Earth ‘s Climate, A Uriarte – Basque Government, 2003 – academia.edu
-
[BOOK] Meteorology and Climate, MCC Castillo, MA Jordan – 1999 – books.google.com.
-
[BOOK] Meteorology, WL Donn, JC de Alemany – 1978 – sidalc.net.
-
[PDF] The climate in history, G GARZA, M BARRIENDOS – Sciences, 1998 –
-
Introduction to agricultural meteorology, JL Fuentes Yagüe – Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food…, 1996 – sidalc.net
-
[PDF] Climate and climate change, AL Escardó – RAM (Revista del Aficionado a la Meteorología, 2001 – divulgameteo.es
- [WEB] EnergiaToday: The weather

![Photo of Alocasias: [Cultivation, Irrigation, Care, Pests and Diseases]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/alocasias-cultivation-irrigation-care-pests-and-diseases-390x220.jpg)


