Plant Cell: [Definition, Characteristics, Types and Importance]
What is the plant cell?
 Plants, like animals, are made up of tissues and these by cells. The plant cell is one that makes up the plant kingdom and is made up of a nucleus, membrane and cytoplasm.
Plants, like animals, are made up of tissues and these by cells. The plant cell is one that makes up the plant kingdom and is made up of a nucleus, membrane and cytoplasm.
The cells of plants, fungi, and animals are called eukaryotes: they have a nucleus and other membrane-enclosed compartments.
They differ in their internal parts and in the specializations of their surfaces. Both plant and animal cells share some characteristics, but differ in others.
The plant cell has unique parts since it carries out an exclusive process that is photosynthesis. The interior of a eukaryotic cell is divided into several functional compartments, including a nucleus.
There the eukaryotic cells began life: Eu which means true and Karyon which means nucleus and refers to it. The perfect plant cell consists of a gelatinous mass defended by a cellulosic envelope or membrane.
Inside this mass or membrane is a generally rounded or oval body called the nucleus, as well as different corpuscles or chromatophores, which, as a whole, without the membrane is called protoplasm.
The protoplasm is the lower part of the cell and there are plants in which there is only a mass of protoplasm without a nucleus or chromatophores. The parietal layer of plants that have complete cells is very important for its osmotic properties and this is due to the absorption of water by the cell.
In addition to the nutritional and growth function of the plant, which the cells together with the protoplasm are responsible for, the reproductive power is also concentrated in them, that is, the function of perpetuating the species.
All cells are alike in three ways: they begin life with a plasma membrane, a DNA-containing region, and a cytoplasm. Knowledge about cells only began after the invention of the first microscopes at the end of the 16th century.
What are the characteristics of the plant cell?
Plant cells have various characteristics, including:
- In the plant cell in its immature stage there are several vacuoles that, as they grow, unite and become one large vacuole.
- It has a central vacuole that stores fluids or liquids and allows the movement of molecules.
- It has a cell wall with pores outside the cell membrane, which provides support and allows communication with nearby cells.
- These cells contain chloroplasts that allow photosynthesis to take place and that have chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color.
What are the types of plant cells?
There are three types of plant cells and each one has a specific function:
parenchymal cell
They are called transfer cells and are responsible for supporting the body, storing and transporting the nutrients generated from photosynthesis. They are the most abundant and specialized cells of the plant organism.
collenchyma cells
They form the growing cells and have a primary wall. They are called plastic support cells. Endowed with only one primary wall, they appear during maturity and are typically elongated, giving the tissues traction, flexibility and resistance.
sclerenchyma cells
 They are characterized by being hard, rigid cells, whose secondary walls have lignin, making them waterproof.
They are characterized by being hard, rigid cells, whose secondary walls have lignin, making them waterproof.
In the maturity of the plant they are usually already dead, without cytoplasm, leaving only an empty central cavity.
They have a main defensive role and serve as support and support for the movements of the stems and leaves of the plants.
What are the types of tissues that make up plant cells?
Plant cells have differentiated tissues according to the function that each of them performs:
Growth tissues (meristems)
They are made up of small cells, capable of division and differentiation, which allows the continuous growth of the plant.
Protective tissues (epidermis and peridermis)
They are responsible for protecting and covering the outermost surface of the plant. Fundamental tissues (parenchyma), are the most abundant in the plant cell and are found among the other tissues and fill the spaces between them.
Supportive tissues (collenchyma and sclerenchyma)
The colenchyma act as a support for the young growing organs while the sclerenchyma support and reinforce the walls that have stopped growing.
Conductive tissues (phloem and xylem)
They constitute a set of highly specialized cells that are placed in a row, they have the shape of tubes that are the vascular system and are responsible for carrying fluids throughout the interior of the plant.
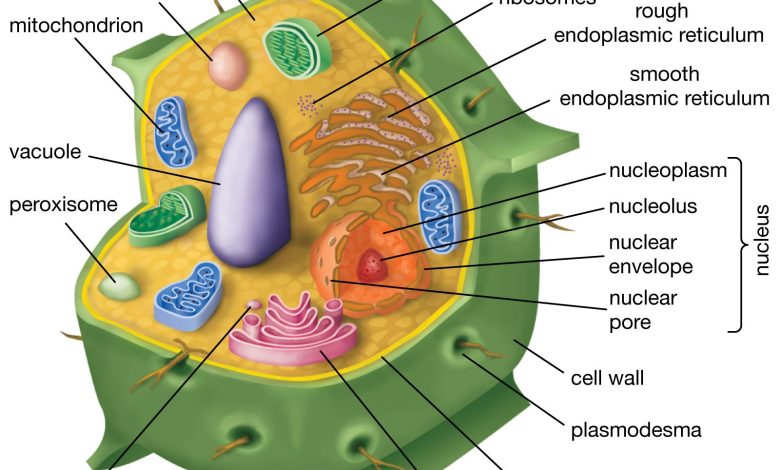
What are the parts of a plant cell?
The parts of the plant cell are:
Cellular wall
It is the layer composed of cellulose that gives shape to the cell and protects the plasma membrane, with a primary and a secondary wall.
Cytoplasm
It is the matter that is located between the plasmatic membrane and the nucleus.
Plasmodesmus
It constitutes the set of channels found in the cell wall, they allow the interconnection to the different cells of a plant and also the exchange of proteins.
vacuole
It is the large cell organelle, surrounded by a plasmatic membrane called tonoplast that contains different fluids. The vacuole allows the plants to remain rigid.
plastids
 They are the part of the cell that produces the synthesis of lipids and amino acids necessary for the process of photosynthesis.
They are the part of the cell that produces the synthesis of lipids and amino acids necessary for the process of photosynthesis.
There are two types of plastids according to their structure, the primary ones are found in a large number of plants and algae; the secondary ones are more complex and are part of the plankton.
They store essential substances for essential processes such as photosynthesis, amino acid or lipid synthesis, and determine the color of fruits and flowers, for example.
They can be chloroplasts (they store chlorophyll), leukoplasts (they allow the conversion of glucose into more complex sugars) or chromoplasts (they store carotenes, a type of pigment).
Chloroplasts
They are characteristic organelles of eukaryotic cells that deal with photosynthesis. Chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy. In addition, they contain a green substance called chlorophyll that gives plants that pigment.
leukoplasts
They store colorless substances and convert glucose into protein or fat.
Chromoplasts
They are a type of plastids that store the colors of some flowers and fruits.
Golgi apparatus
It constitutes a set of 80 dictyosomes in the cell, flattened bags arranged one above the other. Its function is to produce many of the cell’s proteins, store and distribute substances.
Ribosomes
Organelles responsible for synthesizing proteins from the DNA information that reaches them via mRNA (messenger).
Endoplasmic reticulum
Membranes distributed in the cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum, smooth and rough. Substances that participate in the synthesis of proteins and lipids are transported through these membranes.
mitochondria
Wrapped in membranes, they are large organelles where cellular respiration takes place through which ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is produced.
Cellular membrane
A thin layer or bilayer of lipids and proteins that surrounds the cell. On its surface it has tiny pores through which it exchanges substances with the outside.
Cell nucleus
It is the control center and is precisely located in the entire center of the cell. It has much of the genetic content in the form of DNA.
What is the importance of the plant cell?
 The plant cell performs all the essential functions for life like any other type of cell. The nucleus of plant cells contains the hereditary material that is passed from generation to generation.
The plant cell performs all the essential functions for life like any other type of cell. The nucleus of plant cells contains the hereditary material that is passed from generation to generation.
At the same time, they are the point where the essential biochemical functions that synthesize essential molecules are carried out.
Also, they obey the cell cycle of every eukaryotic cell (with a cell nucleus) composed of Interface and the mitotic phase where asexual (mitosis) or sexual (meiosis) cell division takes place.
Without a doubt, photosynthesis, the process responsible for the transformation of solar energy into organic matter, is the cornerstone of life on Earth. To achieve this, photosynthesis creates molecules of ATP and NADPH, the first ones where the chemical energy created is stored.
Unlike the animal cell, the plant cell has a cell wall that provides rigidity and protection to the plasma membrane. However, this wall is not exclusive to the plant cell, since other eukaryotic cells also have it.
Chloroplasts and vacuoles are also inherent in the cells of any type of plant that performs photosynthesis. This organelle is responsible for the green hue of plants and for the transformation of inorganic matter into organic matter from the energy of the Sun.
It is a very important element in nature since it releases the vital oxygen that living beings breathe.
Bibliography and references
- Fragoso, R; Lussier A., (1971) Natural history, life of animals and plants. Seventh Edition, Volume III. Barcelona-Spain: Gallach Institute of Bookstore and Editions, SL
digital database
- Magnaplus.org. Plant tissue. Reproduced from: https://www.magnaplus.org/articulo/-/articulo/RT272/la-celula-y-los-tejidos-vegetales
- Wikipedia. Plant tissues. Reproduced from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tejidos_vegetales



![Photo of Elm Cuttings: [Grafts, Time, Rooting and Planting]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/elm-cuttings-grafts-time-rooting-and-planting-390x220.jpg)
