Sowing Peppers: [Cultivation, Substrate, Irrigation, Care]
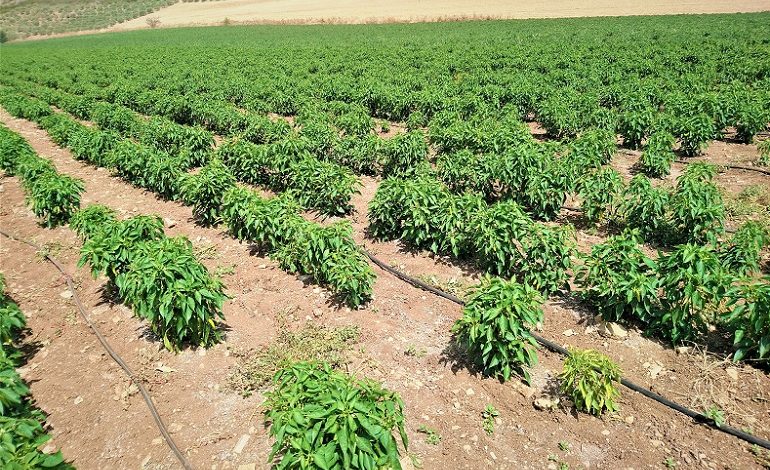

Peppersit is the edible fruit of the plant of the same name. It belongs to the Solanaceae family, it is a type of fruit vegetable and is related to the potato, the tomato and the eggplant.
Its introduction in Europe represented an important advance in culinary customs due to the fact that it was used as a substitute for black pepper and, although its consumption dates back several centuries, the popularity of some varieties that are consumed today are recent.
YesAre you interested in planting peppers?It is important that you know that, like all nightshades, your plant is very demanding in nutrients and requires a good dose of heat.
Although, if you follow this guide, there is nothing stopping you from growing your own peppers at home.
Sow Peppers Step by Step:
- When? Between April and May.
- where? Area that receives a lot of sunlight. At least 7 hours a day.
- Harvest time? About 30 days from the plant or the seed has germinated.

- How do we prepare the land? Removed with a power tiller, pH between 6.5-7. Ideally, there has been sowing of peas before.
- How do we pay? They are demanding. With decomposed organic matter such as manure, well mixed with the soil. Also earthworm humus. Use a compost bin if we have one.
- How do we water? Ideal, with drip.
- How often do we water? They are picky about water. In hot summer, daily about 30-40 minutes. Otherwise every 2-3 days about 30-40 minutes. Look at the leaves to determine if they need more water.
- How do we sow? With seed, we bury about 3mm. We leave a space between seeds of approximately 2.5cm. With campuses we leave a little more space.
- How do we harvest? When the color of the peppers begins to be strong. We cut the stem.
- Good associations? Garlic, cabbage, chard, basil, eggplant, spinach, peas, beans, lettuce, radishes and tomatoes. _
- Bad associations? Cucumbers.
- Diseases and pests? Aphids, spider mites, whiteflies, thrips, woodlice, nematodes, oidiopsis, gray rot and white rot.
 Nowadays, we can find many types of peppers available in the market and, if you wish, you can choose which variety you want to grow based on its size, color or even the level of heat that you like.
Nowadays, we can find many types of peppers available in the market and, if you wish, you can choose which variety you want to grow based on its size, color or even the level of heat that you like.
Practically, for each variety of pepper there is a way to cook it.
It bears high temperatures very well, but is quite sensitive to cold.
For this reason, its cultivation takes place during the summer and part of the autumn, although thanks to greenhouse production or hydroponic crops we can find peppers on the market throughout the year.
Did you know…With green peppers you can prepare a jam, which is very suitable for preparing cakes or accompanying foods such as cheeses.
What do we need to plant peppers?
To sow pepper effectively, we must take into account the following requirements in our crop:
pepper irrigation
To grow pepper,watering should be abundant and regular.However, we must try not to exceed the amount of water.
An excess of watering could cause the flowers to fall.
The soil must remain moist to the touch at all times. This is very important since the pepper needs to be exposed to the sun for a long time.
 The pepper is mainly made up of water, so we must ensure that it is always well watered.
The pepper is mainly made up of water, so we must ensure that it is always well watered.
The ideal for this type of crops isdrip irrigation, this way we make sure that it does not lack water without flooding the plant.
Optimum humidity is achieved by watering every 1-2 days. But keep in mind that peppers grown in hotter climates may need more water.
About 2.5 to 5 cm. of water per week is the recommended amount, under moderate growing conditions.
Remember that the pepper supports high temperatures well as long asthere is adequate humidity, so before planting, make sure that the land where you plant them drains easily.
If your garden tends to flood, you need to do everything you can to fix it.
You can create slopes so that the water runs off to one side and install gutters to make it easier to collect the water.
Another effective technique is to create mounds of soil and plant the peppers on top of them, so less water will collect at the bottom of your plants.
At planting time, add a good amount of mulch, compost, peat or manure to fluff up the soil and aerate it. If you also add river sand and mix it well with the soil, the result will be favorable.
In extreme cases, it is best to install a network of drainage pipes.
Did you know…For reasons still unknown, people who are allergic to latex may also be allergic to capsicum.
Climate when growing peppers
They are quite sensitive
to temperature changes. If there is a discrepancy between night and day temperatures, this can alter the development of flowers.
It does not like frost at all, so in autumn and winter it is only possible to grow it in greenhouses.
weather tips
Always wait for the beginning of spring to plant peppers.
 The optimum temperature for good growth variesbetween 20 and 26 ºC.
The optimum temperature for good growth variesbetween 20 and 26 ºC.
High temperatures cause flowers to drop, while lower temperatures produce small and even malformed peppers.
The pepper is a very demanding plant in light, especially in the early stages of development and during flowering.
Requires at least6 hours of light for your crop.Although it does not require as much sun as the eggplant, it is more demanding than the tomato.
Full, direct sun will provide enough light and heat to stimulate the growth of your plants.
The average temperature for a good growth is between 20 and 26º C, however it supports higher temperatures well, as long as the humidity is adequate.
You can protect your plants with covers with thermal insulation on very cold nights. These covers trap the heat the peppers need, while also providing a barrier against rain and predators.
The Nutrients
PeppersThey are very demanding in terms of nutrients.especially potassium. For the same reason, a large subscriber is required.
Nutrient Tips
Comfrey leaves can be composted to raise potassium levels.
Potassium absorption is decisive for the coloration and quality of the fruits, and increases progressively until flowering.
 Regarding nutrition, the pepper is also a very demanding plant in nitrogen during the first phases of its cultivation, although this demand decreases after the harvest of the first green fruits.
Regarding nutrition, the pepper is also a very demanding plant in nitrogen during the first phases of its cultivation, although this demand decreases after the harvest of the first green fruits.
If possible, plant them in a plot of land where you just planted peas.
On the other hand, it is also very demanding in phosphorus with the appearance of the first flowers and with the maturation period of the seeds.
The pepper is very demanding in terms of magnesium nutrition, increasing its absorption during maturation.
The most recommended fertilizers are simple fertilizers in the form of soluble solids (calcium nitrate, potassium nitrate, ammonium nitrate, monopotassium phosphate, potassium sulfate, magnesium sulfate), and also in liquid form (phosphoric acid, nitric acid).
What is known as carbonic fertigation is also recommended, which consists of the use of carbonated water for irrigation.
The use of carbonated water offers certain advantages in pepper cultivation, such as soil acidification, which facilitates the solubility and correct absorption of nutrients. It also increases the quality and number of fruits and replaces the use of nitric acid.
It is recommended that you make sure to measure the pH of the soil and adjust the need if necessary.
Optimum pH values rangebetween 6.5 and 7,although it can resist certain conditions of acidity up to 5.5 and in sandy soils it can be grown with pH values close to 8.
Did you know…The ACE pepper is a hybrid pepper developed in the laboratory that has more antioxidants and vitamins than normal. It is so called because it has vitamins A, C and E.
the substrate
The most suitable soils for pepper cultivation are sandy ones, particularly deep and well drained. It is ideal that they berich in organic matter.
The pepper has a deep pivoting root system, with numerous horizontal roots that can reach a length between 50 centimeters and 1 meter.
Substrate Tips
If the ground is very rocky or prone to flooding in the rain, consider building a raised bed to plant your peppers.
 The substrate must have good drainage, be well aerated and soft.
The substrate must have good drainage, be well aerated and soft.
Mulching should be maintained throughout the growing process, as it helps regulate temperature and humidity.
The ideal is to mix the soil with a large amount of homemade organic matter such as compost or fertilizer, and keep it always moist.
The pepper is less resistant than the tomato and the aubergine to the salinity of the soil and the irrigation water.
For cultivation in fields or containers, a minimum capacity of 15 liters is recommended.
Each pepper plant requires about 2 feet of space to grow. Therefore, you may want to plant the peppers in only one plant per pot.
Likewise, it is recommended that the container where you place it be ceramic, since it retains heat better. It must have good drainage.
Before planting the peppers
The seeds
The seed to sow peppers is extracted from the ripe fruits.
pH
Optimum pH values range between 6.5 and 7.
If the soil is too acidic, add limestone or wood ash to neutralize the pH.
If the soil is too alkaline, incorporate pine shavings or peat moss to adjust the pH.
The fertilizer
 Before planting peppersapply compost or earthworm humus
Before planting peppersapply compost or earthworm humus
to the earth.
If you prefer, you can apply a little 5-10-10 fertilizer to the soil to keep the plants fed. Don’t overdo it, as too much fertilizer can cause nutrients to be lost in the soil.
Other fertilizers that you can use are fishmeal or poultry manure.
Another recommendation is to bury a few matches upside down around the pepper plants to give them some of the sulfur they require.
Where to plant peppers?
Preferably outdoors. In direct sun, at leastfor 7 hours.
In case of planting peppers in a pot, make sure that it is at least 15 liters in capacity and more than 60 cm in circumference so that the plant has enough space to grow.
To plant your seeds in a pot, you must follow the same steps as for planting them outside.
How do we prepare the land?
The soil must have good filtering. Also, it should be loose enough, without being compressed.
If you plant peppers in a pot, a good recommendation is to mix two parts of soil and one part of sand. The soil offers your plant the nutrients it needs, while the sand controls humidity.
planting peppers
On what date?
During spring.Although in some warmer regions it can be advanced one or two months.
These dates are for Spain.For Latin America, we must add 6 months to the indicated dates, that is, for October and November.
The process
Try to keep them at a temperature of approximately 23 ºC, this will favor the success of germination.
Make a hole 3 millimeters deep in the soil and place the seed.
Keep a distance of 2.5 centimeters between one hole and another.
Cover the seeds with a thin layer of soil and water them carefully so that the water does not puddle.
Did you know…The original name of the pepper is ají and that is how it is still known in different parts of South America.

The first shoots
On average, the seeds take between 10 and 15 days to germinate.
If you have planted in a pot or nursery, you should remove them from the tray when the shoots are two months old.
To confirm this, check your plants: when they have two levels of leaves, it means that they are big enough to be transplanted.
the transplant
 Transplant only if the weather is warm enough.
Transplant only if the weather is warm enough.
Keep in mind that peppers are very delicate plants that need to be gradually exposed to the outdoors before being transplanted.
So a couple of weeks before you transplant them, start gradually exposing them to the weather outside.
You can place them by exposing them to the outside for just a few hours a day, slowly extending the number of hours as they grow.
Place the plants with a separation between them of 60 cms. If the separation is less, you run the risk that they do not receive enough light and the air does not circulate properly.
To find out more, read our guide: Planting chillies in Spain.
How do we guide the pepper plant?
You will need to insert posts to help the plants stand upright, as pepper plant stems are not particularly sturdy.
In addition, the tutorado also improves the conditions of ventilation and luminosity.
Pruning and thinning
Pruning can be a useful practice to improve the conditions of the plant, especially if it is grown in a container.
Pruning promotes air circulation between plants and produces better fruit.
If thick peppers are desired, thinning is recommended, leaving only 2 or 3 fruits per plant.
Being multiannual, the plant can be preserved by pruning it. The following year, it will sprout giving new peppers.
The harvest and collection of the pepper
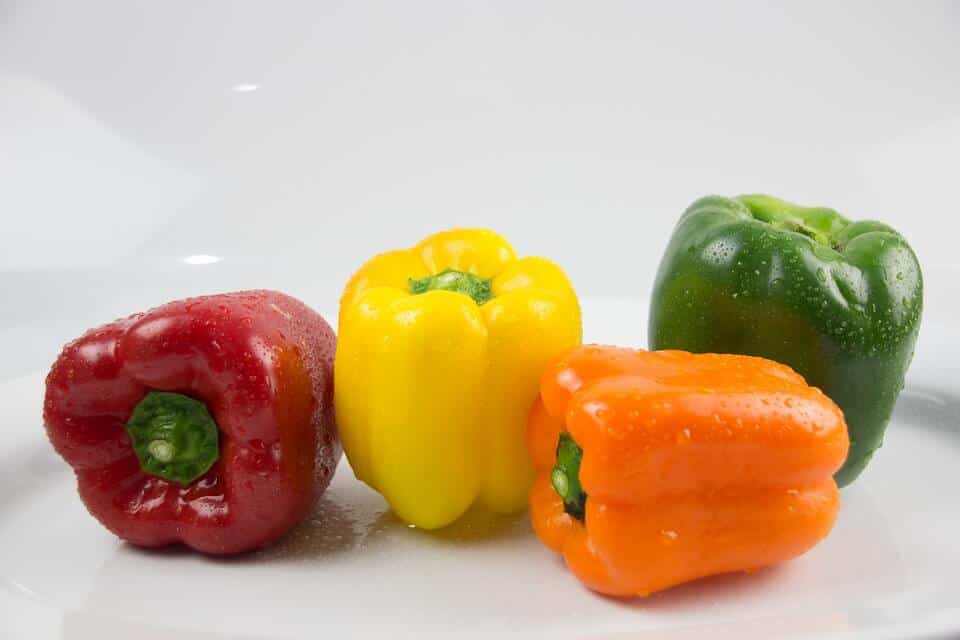 It is a medium-long cycle crop, so the harvest begins 30 days after transplanting.
It is a medium-long cycle crop, so the harvest begins 30 days after transplanting.
The fruit is harvested immature, since harvesting can be paralyzed. This does not apply, of course, for the peppers dedicated to drying (chilli, paprika), which are left on the plant.
The time of harvesting the pepper can be determined by its visible physical characteristics:
Pimientos Verdes: tamaño, firmeza y color del fruto. Los pimientos maduros presentarán un tono verde profundo más oscuro que el tallo de la planta.
Pimientos de Color: un mínimo de 50% de coloración.
Retira los pimientos maduros usando un cuchillo afilado o tijeras de jardín. Córtalos por la parte de arriba del tallo.Si halas los pimientos puedes dañar los tallos o las raíces.
Para saber más, lee: Cuántos pimientos da una planta.
La postcosecha
Los pimientos se deben enfriar lo más rápido posible para reducir pérdidas de agua y evitar que se arruguen.
Los pimientos verdes se mantendrán frescos en el refrigerador hasta 2 semanas.
The favorable associations of the pepper
It pairs very well with garlic and cabbage.
It is compatible with chard, basil, eggplant, spinach, peas, beans, lettuce, radishes, and tomatoes.
unfavorable associations
On the other hand, it is incompatible with cucumber. You should also not plant peppers near vegetables like fennel and kohlrabi.
Common Pepper Pests and Diseases
The pests
- The most common pests that can appear during pepper cultivation are caterpillars, nematodes, whitefly, red spider mite, aphids, thrips and cochineal.
- Aphid: to prevent it can be associated with basil. If eradication is required, potassium soap and vegetable insecticides can be used.
- Red spider: It appears especially when there are high temperatures with low humidity and/or excess nitrogen in the farmland. To combat it, it is recommended to water the pepper at night by sprinkling to maintain humidity, and to use natural insecticides.
- White fly: To prevent it, the underside of the leaves can be sprayed with 1% potassium soap with rain or distilled water.
- Trips: These are flying insects that leave white spots with black dots on the leaves. To combat it, a combined application of neem extract and potassium soap is recommended.
- Mealybugs: It is one of the most difficult pests to control since its body is covered with white waxy excrescences, chemical treatments are not very successful.
Biological control can be done through natural enemies, such as Cryptolaemus montrouzieri, a predator of this type of insect. The release is done 15 days after any treatment, periodically in spring or early summer.
Nematodes: They are treated with steam sterilization and solarization, which consists of raising the temperature of the soil by placing a transparent plastic sheet on the soil for a minimum of 30 days. You can also place a cardboard ring around the base of each stem to protect the plant.

![Photo of White Mold in your Garden: [Identify, Prevent and Treat]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/white-mold-in-your-garden-identify-prevent-and-treat-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Elm Cuttings: [Grafts, Time, Rooting and Planting]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/elm-cuttings-grafts-time-rooting-and-planting-390x220.jpg)
![Photo of Armuelle: [Cultivation, Irrigation, Care, Pests and Diseases]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/armuelle-cultivation-irrigation-care-pests-and-diseases-390x220.jpg)