Celinda: [Characteristics, Cultivation, Care and Disadvantages]

Important points when sowing a Celinda:
- When? Celinda can be multiplied by cuttings planted in spring or August and by layering at the beginning of summer.
- Where? Any corner of the garden where it can receive sunlight and have some shade will be the most suitable.
- How do we water? Celinda requires moderate watering, and once its first year has passed, watering should be adjusted so that the plant is stronger and more vigorous.
- How often do we water? Experts recommend watering 3 times a week during the summer and only 2 waterings a week the rest of the year.
- What care does it require? It is not very demanding with the condition of the soil or substrate and it is enough for it to be fertile and drain well. A universal substrate can also be used.
- What pests and diseases affect you? Celinda can be affected by the presence of aphids and mealybugs, as well as by diseases caused by fungi.
What characteristics does the celinda plant have?
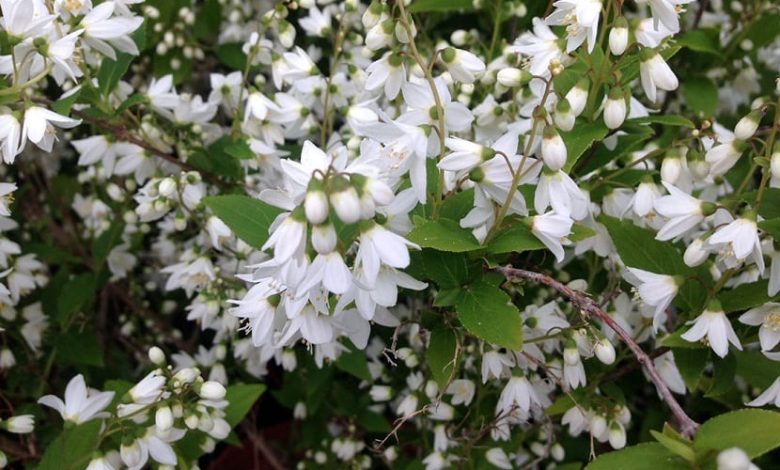
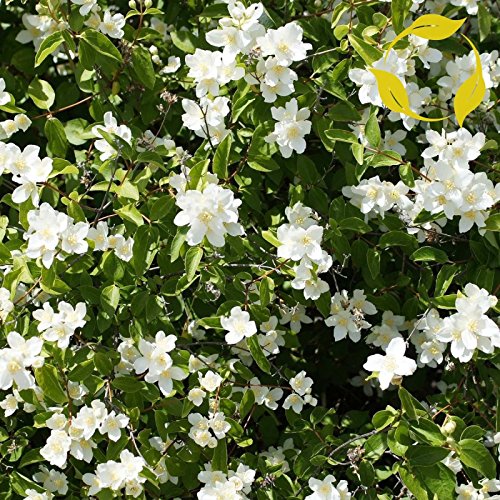 The celinda is a bushy plant of the saxifragaceae, with stems up to two meters high and receives the scientific name of Philadelphus coronarius.
The celinda is a bushy plant of the saxifragaceae, with stems up to two meters high and receives the scientific name of Philadelphus coronarius.
It can reach a height between one to three meters and has a brown bark.
It is a plant that has its origin in southeastern Europe and Asia.
Its leaves are simple and deciduous, oval or elliptical from 4 to 9 cm. pointed, with short petiole, entire or toothed edge, with patent veins and intense green color.
The celinda flowers are hermaphrodite arranged in clusters, with an ovate calyx tube and a corolla with four to five petals, white, very fragrant, with many stamens and four or five styles.
The fruit consists of a capsule with four dehiscent cavities containing numerous tiny seeds. It is a very melliferous and dye-producing plant whose woody stems were used in ancient times to make musical instruments such as the flute.
The scientific name of celinda, Philadelphus, comes from the Greek meaning brother or fraternal. It is also known by the common name of coronaria because, according to scholars on the subject, celinda was used to decorate crowns.
Due to its beauty and fragrant blooms that are reminiscent of orange blossom, celinda is also used to decorate parks and gardens. The celinda also receives the names of celindo, philadelphus, false jasmine, false orange tree or syringe and is found in the temperate or cold-temperate zones of the world.
Numerous celinda hybrids are currently cultivated, which differ in the variegation of the leaves and the purple tones of its flowers. The scientific name of the plant comes from the Greek and is said to be dedicated to Ptolemy II Philadelphus, who reigned in the 3rd century BC.
Did you know…?The story says that according to Egyptian custom Ptolemy married his sister and had himself worshiped as a divinity in life together with his sister-wife, as Philadelphian gods, that is, brother-gods who love each other.
Hence, celinda is considered a plant that represents the fraternal feeling of love, friendship and brotherhood.
When to sow celinda?
Celinda can be multiplied by cuttings planted in spring or August and by layering at the beginning of summer.
Where to plant celinda?
The place for planting celinda will be the one that best suits its light needs. Therefore, any corner of the garden where it can receive sunlight and have some shade will be the most suitable.
How do we water the celinda?
 Celinda requires moderate watering, and once its first year has passed, watering should be adjusted so that the plant is stronger and more vigorous.
Celinda requires moderate watering, and once its first year has passed, watering should be adjusted so that the plant is stronger and more vigorous.
It is recommended never to water neither the flowers nor the leaves of celinda to avoid fungal diseases in the plant.
How often do we water the celinda?
 The frequency for irrigation of celinda will depend on the area and the climate where the crop is located.
The frequency for irrigation of celinda will depend on the area and the climate where the crop is located.
Experts advise watering three times a week during the summer and only two waterings a week the rest of the year.
In those areas with a lot of rainfall, it is recommended to reduce the frequency or increase the irrigation if it is very dry regions.
How to plant a celinda step by step?
- Cut a celinda cutting about 40 cm from a mature, healthy and robust plant. Spray the cutting with hormones for rooting.
- Select a container with holes that has good drainage capacity.
- Fill with universal substrate for flowering plants and 30 percent perlite, previously moistened.
- Water moderately and without flooding to maintain the humidity of the crop.
- Locate the plant in full sun or semi-shade.
- Fertilize once a month with organic fertilizers.
- Transplant every two years during the spring.
What care does the celinda need?
Celinda is a very easy plant to care for and grow. It is not very demanding with the condition of the soil or substrate and it is enough for it to be fertile and drain well.
A universal substrate can also be used. It grows easily in sun or semi-shade. It is a plant resistant to low temperatures, although it prefers temperate climates.
Caution is recommended when pruning celinda, since its flowers are born from the stems of the previous year. For this reason, old shoots should be removed shortly after flowering has finished.
Fertilize with organic fertilizers, from early spring to late summer or early fall.
What pests and diseases affect celinda?
 insects and pests
insects and pests
Celinda can be affected by the presence of aphids and mealybugs, as well as by diseases caused by fungi.
Aphids suck the sap from the stems and are dangerous for celinda because they reproduce quickly and can even kill the plant.
To eliminate aphids, it is recommended to apply a mixture of water with a little biodegradable soap and clean the entire plant with a cloth.
Mealybugs stick their sucking beak on celinda leaves, stems and fruits and suck its sap which they then excrete as a sugary liquid known as molasses.
fungal diseases
Fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and rust can affect celinda.
Powdery mildew is a whitish hair that acts on celinda leaves and stems, normally located in the shade and in areas or times of high environmental humidity. Rust is one of the most serious fungal diseases of crops, especially coffee, but it can also affect celinda.
To prevent fungal diseases, experts recommend dusting celinda with copper or sulfur powder. Many of the pests and diseases can be deadly for celinda, so the best cure is prevention and control of risks.
Bibliographic references
- Plants and popular culture: Ethnobotany in Spain. Names of plants used as personal names, R Morales Valverde – 1996 – digital.csic.es
- Didactic catalog of the most characteristic flowering plants around the city of Albacete, second part, AV Franzi, RM Cantos – Essays: Journal of the Faculty of …, 1989 – dialnet.unirioja.es
- The garden of the Institute of the Canary Islands, DGC MARICHAL, FJR GARCÍA – museocabrerapinto.es
- Landscaping, Lighting and Exterior and Interior Decoration, JMF Veiga – 2020 – books.google.com







![Photo of Planting an Orange Tree: [Forms, Care, Substrate, Irrigation and Pests]](https://www.complete-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/planting-an-orange-tree-forms-care-substrate-irrigation-and-pests-390x220.jpg)